Water from lakes/rivers are not drinkable unless treated correctly because surface runoff and sewers carry contaminants into the waterways that are connected to those lakes/rivers.
It is only drinkable if treated chemically to kill harmful bacteria and pathogens.
Surface water in lakes, rivers, swamps and other bodies of water often contain impurities that make it look and smell bad. It also contains harmful chemicals, bacteria, and other microorganisms. Chemicals and boiling (pasteurization) can kill most pathogens/bacteria.
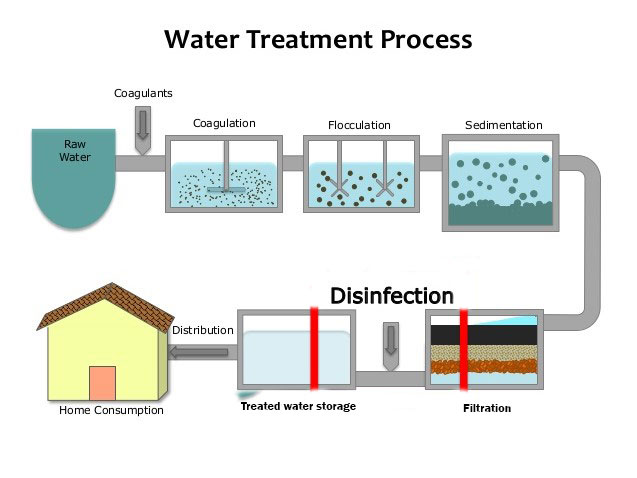
Municipal Water Treatment Process
1. Screening
Water is taken from appropriate lakes/reservoirs. Large solids like branches are taken out.
2. Coagulation and Flocculation
Coagulation is the process of adding chemicals with a positive charge to the water (usually alum, or more specifically, aluminum sulfate).
Flocculation is the process of mixing the water in a way that promotes the forming of floc (clumps of alum and sediment) and helps to settle the particles.
3. Sedimentation/Flotation
Sedimentation is the process of leaving floc to settle to the bottom of the holding tank, leaving the water at the top the clearest. Water is taken from the top to the next step.
Flotation is the process of pumping air from the bottom of the tank. The air bubbles carry floc to the top, where a rod sweeps across and gathers the floc. The water at the bottom is the clearest, so water is taken from the bottom to the next step.
4. Filtration
Water passes through numerous filters, usually involving sand, charcoal and gravel. Sand filters have 3 layers, coarse to fine.
This process is to remove any remaining waste solids and small pieces of floc that is still in the water. After this step, the water is clear, colourless, and odourless.
5. Disinfection
The main method of disinfection is chlorination. It kills the remaining parasites, bacteria, and viruses. It stays in the water during transportation so it prevents any microorganisms from entering the clean, drinking water.
6. Storage/Transport
The clean water is either stored in places like water towers or directly moved to wherever it is needed.
Other Ways of Water Treatment
Desalination
- Solar Evaporation
- heating salt water
- Freezing
- the ice that forms do not hold salt, but do need to be rinsed with freshwater because the ice crystals may contain pockets of salt
- Reverse Osmosis
- applying pressure to the salt water, pushing it through a semi-permeable membrane to turn into freshwater
- contaminants cannot pass through the membrane
- goes from high salinity to low salinity
- uses a lot of energy because reverse osmosis is active transport
- applying pressure to the salt water, pushing it through a semi-permeable membrane to turn into freshwater
Brine is a byproduct of desalination that contains high amounts of salt.
Iodine
- added to water in crystallized form or in tablets
- kills most of the pathogens present in natural freshwater sources
Boiling
- heating the water to boiling inactivates most pathogenic bacteria if done long enough
- does not remove most pollutants in the water and does not leave any residual protection

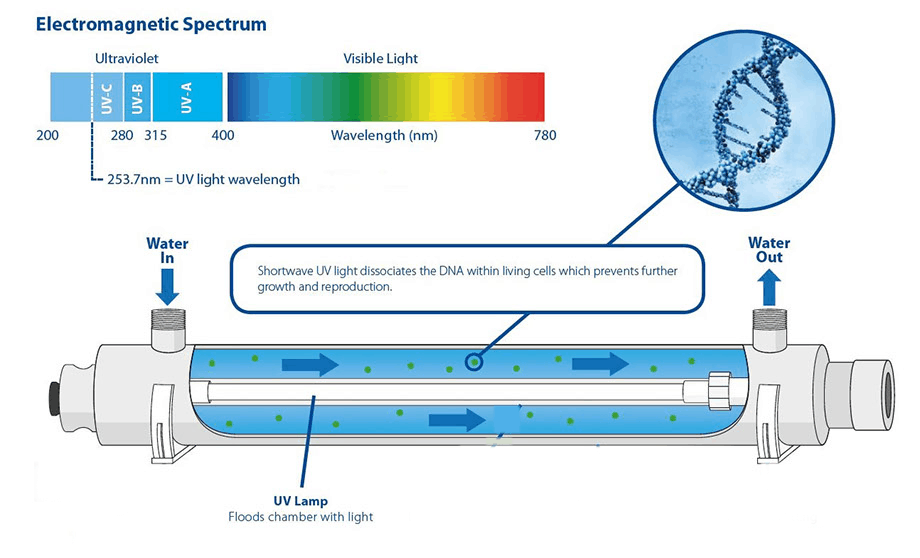
UV Radiation
- scrambles the DNA of bacteria, making them unable to reproduce, thus far less harmful
- doesn’t do anything else
Ozone
- microbes are destroyed by ozone gas (O3)
- also reacts with long-chain carbon (organic) molecules, breaking them down into simpler and (usually) less harmful molecules
- simply degrades into oxygen when done, thus not leaving any harmful residue behind
Activated Carbon
- usually a filter
- removes contaminants, odor and taste in water
- usually attached to faucet or under sinks in home
Bioremediation
- uses microorganisms that metabolize pollutants
- those microorganisms could digest highly radioactive waste, though not heavy metals like lead
- the bacteria spits out enzymes that breaks down fats, oils, starch, sugar and grease for the bacteria to eat
- secretes CO2and water as byproduct
- reproduce and repeat
Many fungi + plants can reduce/absorb toxins.
Sunflowers can get rid of radioactive material.
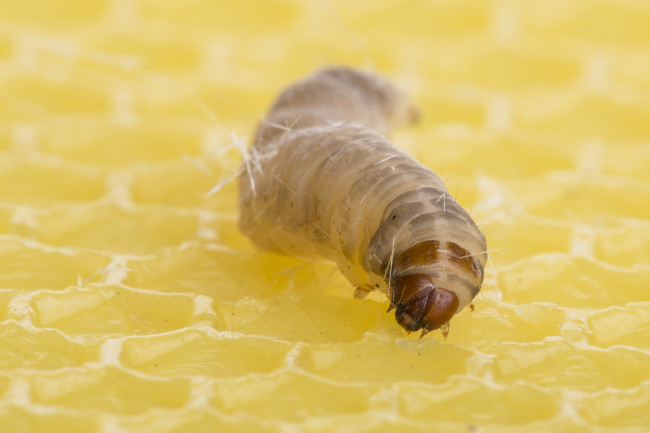
An enzyme in the wax moth caterpillar can eat away polyethylene.