Organs systems are different organs working together
≿━━━━༺❀༻━━━━≾
Nervous System
- Function:
- responds to changes impacting the body
- coordinates the function of every part of the body
- Contains:
- brain
- spinal cord
- nerves
- sensory organs
- eyes, ears, nose, etc.
- Major Tissues:
- epithelial
- nerve
- connective
The sensory organs send signals via the spinal cord to the brain. The brain processes the information and orders the body to respond appropriately. ↵
Muscular System
- Function:
- enables movement and locomotion
- Contains:
- muscles
- tendons
- ligaments
- muscles
- Major Tissues:
- epithelial
- muscle
- nerve
- connective
The muscles contract, resulting in movement. They also move substances through the body. ↵
Circulatory System
- Function:
- transports nutrients, dissolved gasses and waste throughout the body
- Contains:
- heart
- blood vessels
- blood
- Major Tissues:
- epithelial
- muscle
- nerve
- connective
The heart pumps the blood filled with nutrient/dissolved gasses/waste to wherever they should go via blood vessels. ↵
Digestive System
- Function:
- breaks down food into nutrients for the circulatory system to transport
- Contains:
- mouth
- salivary glands
- esophagus
- stomach
- liver
- gallbladder
- pancreas
- small and large intestines
- anus
- Major Tissues:
- epithelial
- muscle
- nerve
- connective
The mouth breaks apart the food into smaller pieces. The salivary glands release saliva to break down the food molecularly. The esophagus continues to make the food smaller. The stomach releases acid and enzymes to break down the food on a molecular level. The liver extracts what nutrients are needed and makes sure everything is not toxic. The gallbladder breaks down fats. The pancreas breaks down the sugars, fats and starch. The intestines digest food even more and leaves only waste. The anus excretes waste.↵
Skeletal System
- Function:
- support for body
- Contains:
- bones
- cartilage
- Major Tissues:
- epithelial
- muscle
- nerve
- connective
The bones for a skeleton, which everything else rests/connects on. Also protects other organs. ↵
Excretory System
- Function:
- to excrete waste materials from the body
- Contains:
- kidney
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- Major Tissues:
- epithelial
- muscular
- nerve
- connective
The kidney sends the waste liquids to the urinary bladder via the ureters. The urinary bladder stores it until the body sends signals for the urine to be released, by the urethra. ↵
Respiratory System
- Function:
- exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide between blood and the outside environment
- Contains:
- lungs
- windpipe
- blood vessels
- Major Tissues:
- epithelial
- muscle
- nerve
- connective
Air is brought in and out of the body by the windpipe, which sends the air to the lungs. The lungs filter the air and send filtered gases to the blood vessels which goes all over the body. ↵
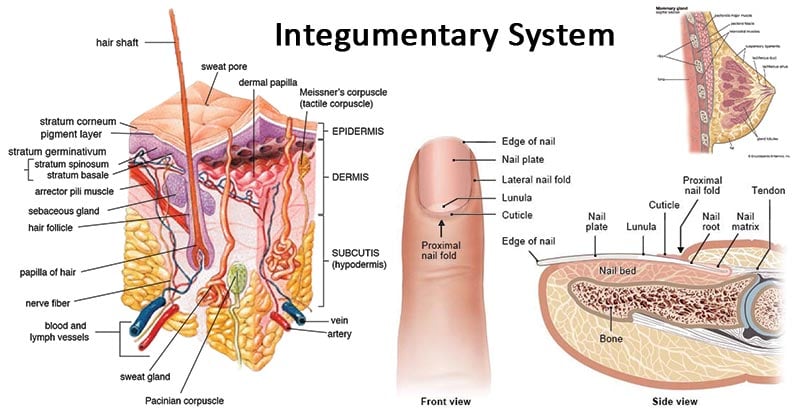
Integumentary System
- Function:
- protect body
- maintain normal body temperature
- Contains:
- skin
- hair
- nails
- sweat glands
- Major Tissues:
- epithelial
- muscle
- nerve
- connective
The skin protects the parts inside it from getting bruised/damaged. Hair covers the skin to provide warmth. Nails protect fingers from outside dangers. Sweat glands prevent the body from getting too overheated. ↵
Immune System
- Function:
- defense against threats to the body
- Contains:
- most components of body
- Major Tissues:
- epithelial
- muscle
- nerve
- connective
The First Line of Defense
- physically prevents threats from entering
- mucus membrane/skin/etc.
- sweat creates harmful to pathogen acidic barrier
- flushing effect excretes invaders
- sneezing/runny nose/vomit/fever
- mucus membrane traps pathogens and attempts to get rid of them
Second Line of Defense
- inflammatory system
- histamine is released when tissues are injured/infected
- blood vessels release fluid into the tissue, causing swelling which signals to not use that body part and let it heal
Final Stage
- Immunity
- white blood cells (lymphocyte, t-cells, antibodies, etc.) go out to search for invaders
- phagocytosis happens when they find them ↵
Pathogens adapt to the immune system, and the immune system adapts to them.
Root System
- anchors the plant
- intakes water and nutrients from the soil
- stores food
- some reproduce asexually ↵
Shoot System
- aids photosynthesis
- support for leaves
- transports substances
- flowers for sexual reproduction ↵
/circulatory_system-56e73fe45f9b5854a9f962fc.jpg)


![DIAGRAM] 8th Grade Respiratory System Blank Diagram FULL Version HD Quality Blank Diagram - PC2REPAIR.YOSHI-SUSHI-ARGELES.FR](https://healthiack.com/wp-content/uploads/Respiratory-system-diagram-unlabeled-1443.jpeg)
![Types of Root System... [OUTDATED] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/cEXHP9oXBGQ/maxresdefault.jpg)
